Stata: Reading in Comma Separated Files
30 May 2011#Reading in Comma Separated Files#
This post will show how to read in comma separated files (also known as .csv files) into Stata. I will show you how to use both syntax and point-and-click.
##Syntax##
You can import csv files using the insheet command.
insheet using "auto.csv", comma clear
The using auto.csv statement just tells Stata the file name of the csv file. If the csv file is not in your working directory, then you will need to provide the entire filepath or cd to the directory with the csv file. I typically include the option comma. This tells Stata that the file is a csv file. This isn’t necessary but it will speed up the insheet command (only an issue if the csv file is pretty big). However, the primary reason I put it in there is to make the code more readable (i.e., so that I know from the code that I read in a csv file, which is particularly important if the file extension is something other than csv). I also add the clear option to clear out any data that are currently in memory.
##Point-and-Click##
We can import csv files by using the Import submenu under the File menu. We’ll select ASCII data created by a spreadsheet under the Import submenu.
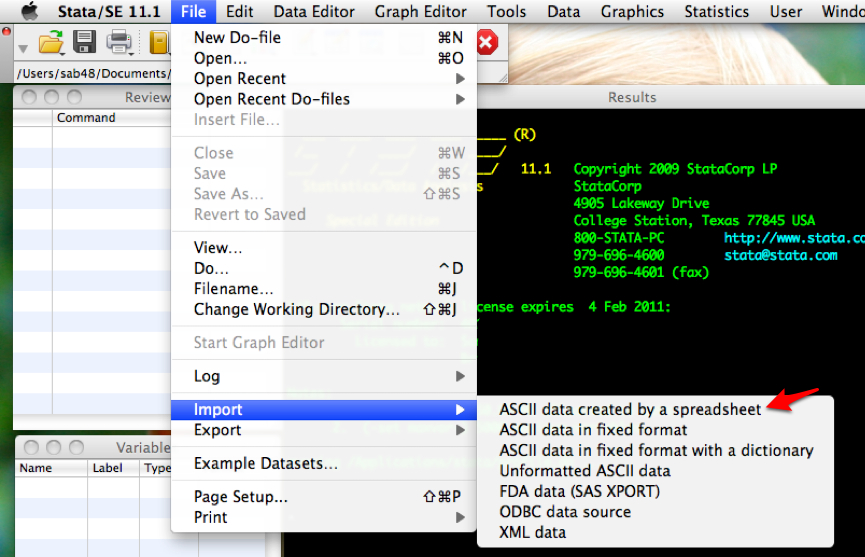
This will open the following dialog menu.
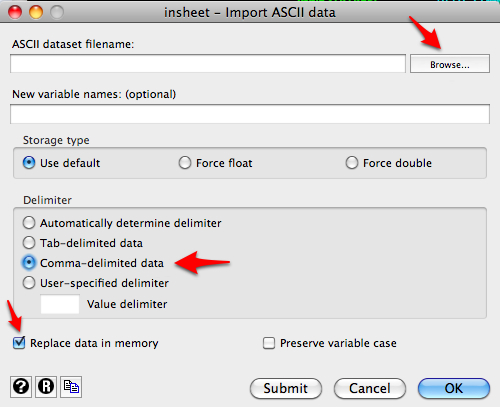
Click on Browse to select the csv file saved on your computer. Select Comma-delimited data. I’ve also selected Replace data in memory to clear out any data loaded into Stata already. If you need to add variable names, you can add them in the dialog box.
Now your data will be read into Stata and ready to use.